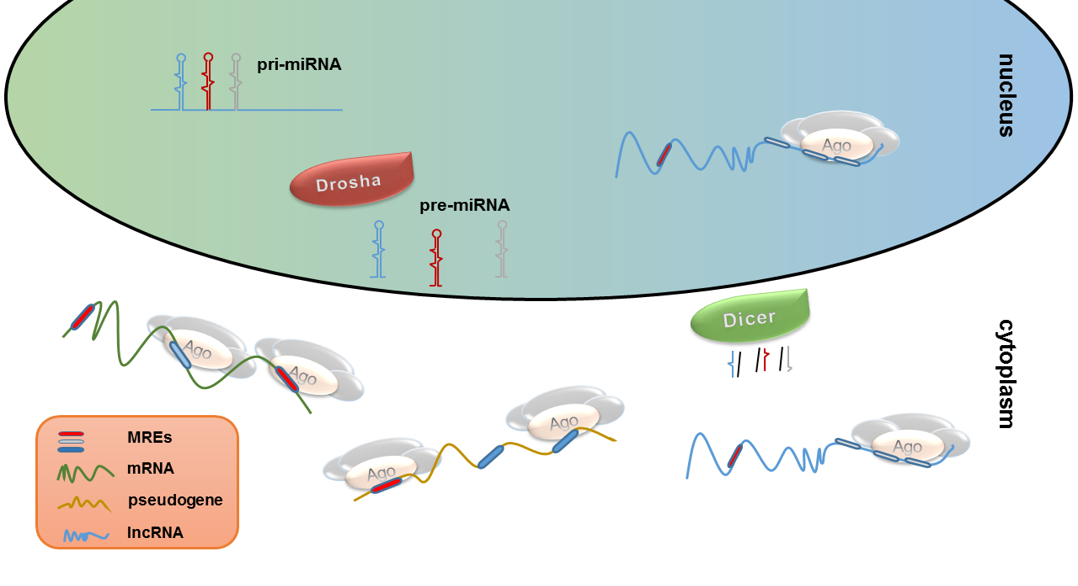
MicroRNA research has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation, uncovering previously hidden layers of complexity in biological systems. Pioneering work by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun and his colleague Victor Ambros in the early 1990s marked a significant breakthrough in this field, earning them recognition with the 2024 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine. Their initial discoveries, centered around microRNAs in the C. elegans roundworm, have far-reaching implications, showcasing how these tiny molecules influence not just worms but potentially all multicellular organisms, including humans. As the scientific community embraces the potential of microRNAs, research has gained momentum, supported by crucial federal research funding that has underpinned decades of exploration and innovation. With ongoing clinical trials exploring microRNA therapies for diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s, the impact of their findings continues to grow, making microRNA research a cornerstone of modern genetics and medicine.
The exploration of small non-coding RNAs, particularly microRNAs, has emerged as a vital area of study within the field of molecular genetics. Early investigations led by esteemed scientists, including Gary Ruvkun, have revealed the intricate roles these RNA molecules play in regulating gene expression across various species. This avenue of research not only enhances our comprehension of biological processes but has also opened new therapeutic pathways for treating a multitude of diseases. With significant advances stemming from federal investment in scientific inquiry, alternative RNA therapies are being developed and tested, showcasing the crucial relationship between foundational research and clinical applications. As researchers delve deeper into the mechanisms of microRNAs, the potential to reshape our approach to medicine continues to expand.
The Groundbreaking Discovery of microRNA
In 1992, the landscape of molecular biology shifted dramatically when Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros unearthed the function of microRNA through their studies on the C. elegans nematode. This tiny class of RNA molecules plays a pivotal role in gene regulation by silencing specific messenger RNAs, thereby influencing the expression of genes at a fundamental level. Initially, their findings weren’t met with widespread acclaim; however, the implications of their research have since expanded, revealing the intricate layers of genetic control beyond what was previously understood.
By publishing their groundbreaking discovery in the journal *Cell* in 1993, Ruvkun and Ambros not only opened up new pathways in gene regulation but also laid the groundwork for a burgeoning field of research. Their work highlighted how microRNA can contribute significantly to developmental processes, cell differentiation, and even responses to stress in organisms, including humans. This foundational research ultimately led to a revolution in genetics, paving the way for countless studies focusing on the roles of microRNAs in various biological contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are microRNAs and how do they relate to gene regulation in research?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules that play a critical role in gene regulation by binding to target mRNAs, leading to their degradation or inhibition of translation. This discovery, initially made by researchers like Gary Ruvkun, highlights the complexity of gene regulation beyond traditional methods, fundamentally altering the understanding of genetic expression.
Why did Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros receive the Nobel Prize for their work on microRNAs?
Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros were awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNAs in 1992. Their research showed how these molecules are essential for gene regulation in organisms like C. elegans, paving the way for understanding genetic mechanisms in higher species, including humans.
How has federal research funding impacted microRNA research?
Federal research funding has significantly boosted microRNA research, with Gary Ruvkun noting that approximately 75% of his lab’s funding comes from sources like the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This support has facilitated critical advancements in understanding microRNA’s roles in various diseases, eventually leading to novel therapeutic approaches.
What potential medical applications are associated with microRNA research?
Research on microRNAs has led to potential medical applications in treating conditions such as heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s Disease, and Alzheimer’s. Many therapies leveraging the regulatory functions of microRNAs are currently in clinical trials, reflecting their importance in modern medicine.
How did the discovery of microRNAs change the perception of genetic research?
The discovery of microRNAs reshaped genetic research by introducing a new layer of gene regulation. Initially met with skepticism, this finding has since been recognized as revolutionary, demonstrating that small RNA molecules can significantly influence gene expression and protein synthesis across various life forms.
What is the significance of C. elegans in microRNA research?
C. elegans, a model organism, has been crucial in microRNA research, particularly due to Gary Ruvkun’s early discoveries. Studying this roundworm has provided foundational insights into the mechanisms of gene regulation, which are applicable to more complex organisms, including humans.
What is the relationship between microRNA and the biotech industry?
The discovery of microRNAs has fostered the growth of the biotech industry, with companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals emerging from research efforts in RNA interference. This highlights the direct impact that foundational microRNA research has had on developing innovative genetic therapies and promoting economic growth in biotechnology.
How do microRNAs influence gene expression during development?
MicroRNAs influence gene expression by regulating the stability and translation of target mRNAs. During development, they are critical in controlling the timing and expression levels of genes necessary for proper growth and differentiation of tissues, underscoring their role in developmental biology.
What challenges are currently being faced in microRNA research?
Despite its advancements, microRNA research faces challenges, including the complexity of their interaction networks and the need for more precise delivery methods in therapeutic applications. Moreover, funding constraints could deter young scientists from pursuing careers in this vital area of study.
What do recent advancements in microRNA research indicate about the future of genetics?
Recent advancements in microRNA research indicate a growing recognition of the intricate regulatory networks governing gene expression and their implications for health and disease. As research evolves, it is expected to play a critical role in personalized medicine and the development of targeted therapies.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, which eventually led them to win the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
| Initial Reception | The scientific community was not initially impressed, questioning the significance of their findings. |
| Funding and Research | Their research was largely funded by the NIH, amounting to around $150,000 annually, supporting a small team. |
| Clinical Applications | Current clinical trials are exploring microRNA-based therapies for various diseases, including cancer and heart disease. |
| Evolution of Interest | Interest in microRNA research grew significantly over the years, leading to increased participation in related scientific meetings. |
| Impact on Industry | Basic research contributed to the establishment of companies like Alnylam, focusing on RNA therapeutics. |
| Concerns about Funding | Ruvkun expresses concern over potential reductions in federal funding for science, warning it could drive researchers abroad. |
Summary
MicroRNA research has transformed our understanding of gene regulation since its discovery in 1992. The groundbreaking work of Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros, now celebrated with the 2024 Nobel Prize, highlights the significance of microRNAs in health and disease. Following decades of exploration, these tiny RNA molecules are key players in various biological processes and have opened up new avenues for therapeutic interventions. As clinical trials for microRNA-based therapies expand, their role in modern medicine becomes increasingly vital, underscoring the need for ongoing investment and support in scientific research.